- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Bioactive O^N^O^ Schiff base appended homoleptic titanium(iv) complexes: DFT, BSA/CT-DNA interactions, molecular docking and antitumor activity against HeLa and A549 cell lines†

Read this article at
Abstract
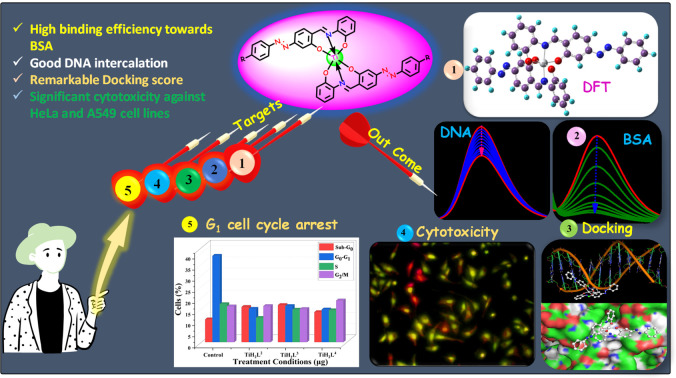
Five new homoleptic derivatives of titanium( iv) have been developed and characterized by physicochemical techniques. Metal complexes, TiH 2L 1 [(C 38H 26N 6O 4)Ti], TiH 2L 2 [(C 38H 24F 2N 6O 4)Ti], TiH 2L 3 [(C 38H 24Cl 2N 6O 4)Ti], TiH 2L 4 [(C 38H 24Br 2N 6O 4)Ti] and TiH 2L 5 [(C 38H 24N 8O 8)Ti], were obtained by treating Ti(OPr i) 4 with appropriate ONO ligands (H 2L 1–H 2L 5) in anhydrous THF as solvent. The electronic structures and properties of titanium( iv) complexes (TiH 2L 1–TiH 2L 5) and ligands (H 2L 1–H 2L 5) were examined by DFT studies. The stability of all synthesized derivatives was assessed by a UV-visible technique using 10% DMSO, GSH medium and n-octanol/water systems. The binding interactions of BSA and CT-DNA with respective titanium( iv) complexes were successfully evaluated by employing UV-visible absorption, fluorescence, circular dichroism (CD) techniques and docking studies. The in vitro cytotoxicity of TiH 2L 2, TiH 2L 3 and TiH 2L 4 complexes was assessed against HeLa (human epithelioid cervical cancer cells) and A549 (lung carcinoma) cell lines. The IC 50 values of TiH 2L 2, TiH 2L 3 and TiH 2L 4 were observed to be 28.8, 14.7 and 31.2 μg mL −1 for the HeLa cell line and 38.2, 32.9 and 67.78 μg mL −1 for A549 cells, respectively. Complex TiH 2L 3 exhibited remarkably induced cell cycle arrest in the G 1 phase and 77.99% ROS production selectivity in the HeLa cell line.
Abstract
Five new homoleptic derivatives of titanium( iv) have been developed and characterized by physicochemical techniques.
Related collections
Most cited references83
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The calculations of excited-state properties with Time-Dependent Density Functional Theory.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer: conformation and dynamics.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found