- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
PaintOmics 4: new tools for the integrative analysis of multi-omics datasets supported by multiple pathway databases

Read this article at
Abstract
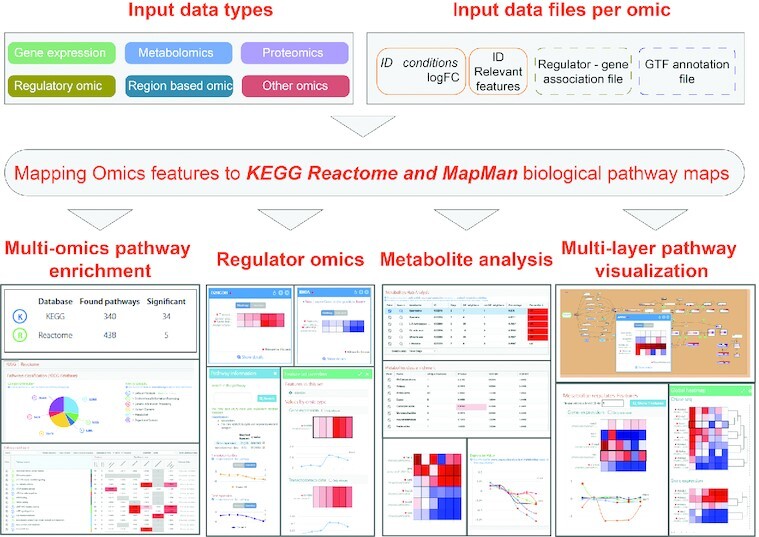
PaintOmics is a web server for the integrative analysis and visualisation of multi-omics datasets using biological pathway maps. PaintOmics 4 has several notable updates that improve and extend analyses. Three pathway databases are now supported: KEGG, Reactome and MapMan, providing more comprehensive pathway knowledge for animals and plants. New metabolite analysis methods fill gaps in traditional pathway-based enrichment methods. The metabolite hub analysis selects compounds with a high number of significant genes in their neighbouring network, suggesting regulation by gene expression changes. The metabolite class activity analysis tests the hypothesis that a metabolic class has a higher-than-expected proportion of significant elements, indicating that these compounds are regulated in the experiment. Finally, PaintOmics 4 includes a regulatory omics module to analyse the contribution of trans-regulatory layers (microRNA and transcription factors, RNA-binding proteins) to regulate pathways. We show the performance of PaintOmics 4 on both mouse and plant data to highlight how these new analysis features provide novel insights into regulatory biology. PaintOmics 4 is available at https://paintomics.org/.
Graphical Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references49
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found