- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical Perspective on Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System in Childhood (cPACNS)
Read this article at
Abstract
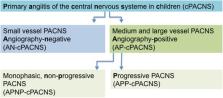
Non-arteriosclerotic arteriopathies have emerged as important underlying pathomechanism in pediatric arterial ischemic stroke (AIS). The pathogenesis and classification of cerebral arteriopathies in childhood are heterogeneous. Different classifications base on (i) the anatomic site; (ii) the distribution and size of the affected vessel; (iii) the time course, for example, transient vs. progressive, monophasic vs. recurrent; (iv) the putative pathogenesis; (v) the magnetic resonance imaging morphology of the vasculopathies. Inflammation affecting the cerebral vessels is increasingly recognized as common cause of pediatric AIS. Primary cerebral vasculitis or primary angiitis of the central nervous system (CNS) in childhood (cPACNS) is an important differential diagnosis in pediatric AIS. Primary angiitis of the CNS is a rare disorder, and the pathogenesis is poorly understood so far. The current classification of cPACNS is based on the affected cerebral vessel size, the disease course, and angiographic pattern. Two large subtypes are currently recognized comprising large- and medium-sized vessel CNS vasculitis referred to as angiography-positive cPACNS and angiography-negative small vessel cPACNS. As the clinical manifestations of cPACNS are rather diverse, precise diagnosis can be challenging for the treating pediatrician because of the lack of vital laboratory tests or imaging features. Initial misdiagnosis is common because of overlapping phenotypes and pediatric AIS mimics. As untreated cPACNS is associated with a high morbidity and mortality, timely diagnosis, and induction of immunomodulatory and symptomatic therapy are essential. Survival and neurological outcome depend on early diagnosis and prompt therapy. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system in childhood differs in several aspects from primary cerebral angiitis in adults. The aim of this article is to give a brief comprehensive summary on pediatric primary cerebral vasculitis focusing on the clinical perspective regarding the classification, the putative pathogenesis, the disease course, the diagnostic tools, and emerging treatment options. A modified terminology for clinical practice is discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references72
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intracranial Vessel Wall MRI: Principles and Expert Consensus Recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Early-onset stroke and vasculopathy associated with mutations in ADA2.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found