- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Role of endoscopic ultrasound in evaluation of unexplained common bile duct dilatation on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Dilated common bile duct (CBD) without obvious cause is a not uncommon finding on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) in patients with unexplained dilated CBD on MRCP.
Methods
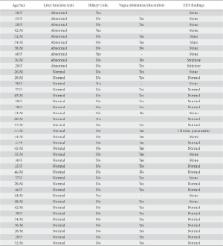
Patients referred for EUS evaluation of a dilated CBD were retrospectively analyzed with respect to serum alkaline phosphatase prior to EUS and subsequent outcome after EUS.
Results
Over a 3-year period, 40 patients (24 males; mean age 38.9±9.9 years) with dilated CBD were retrospectively identified. Ten patients had elevated serum alkaline phosphatase. The diagnosis reached after EUS examination was: CBD stones in 15 (37.5%) with largest size of CBD stone being 9 mm, mass in CBD in 2 (5%), benign biliary stricture in 2 (5%), biliary stricture with underlying chronic pancreatitis in 1 (2.5%) patient respectively. EUS examination revealed normal CBD in 20 (50%) patients and two of these patients had periampullary diverticulum. All the patients with abnormal liver function tests had a detectable CBD pathology whereas 20/30 (66.6%) patients with normal liver biochemistry had normal EUS findings. There was no significant difference in the mean CBD diameter between the groups with demonstrable pathology compared with those without (P=0.64).