- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Systematic Review of Smartphone and Tablet Use by Older Adults With and Without Cognitive Impairment
Read this article at
Abstract
Background and Objectives
A systematic review was conducted to explore the use of smartphones and tablet computers as cognitive and memory aids by older adults with and without cognitive impairment, specifically the effects of smartphone and tablet use on participants’ cognition and memory, and the barriers and facilitators to smartphone and tablet use for cognitive and memory support.
Research Design and Methods
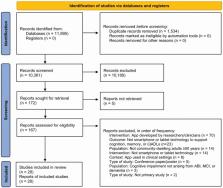
A systematic search of 6 key databases found 11,895 citations published between 2010 and 2021. Studies were included if they involved community-dwelling older adults with or without cognitive impairment arising from acquired brain injury, mild cognitive impairment, or dementia, and if they evaluated everyday smartphone or tablet device use for cognition, memory, or activities of daily living.
Results
A total of 28 papers were included in the narrative synthesis. There was some evidence that the use of smartphones and tablets could aid cognitive function in older adults without cognitive impairment, particularly executive function and processing speed. There was modest evidence that smartphone and tablet use could support memory in both older adults without cognitive impairment and those with acquired brain injury and dementia.
Discussion and Implications
Smartphones and tablets were seen by users as acceptable, enjoyable, and nonstigmatizing alternatives to conventional assistive technology devices; however, current use of smartphone and tablet devices is hindered by the digital literacy of older adults, a lack of accommodation for older adult users’ motor and sensory impairments, and a lack of input from clinicians and researchers. Much of the evidence presented in this review derives from case studies and small-scale trials of smartphone and tablet training interventions. Further research is needed into older adults’ use of smartphones and tablets for cognitive support before and after the onset of cognitive impairment in order to develop effective evidence-based smart technology cognition and memory aids.
Related collections
Most cited references63

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found