- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The impact of type 2 diabetes on bone metabolism
Read this article at
Abstract
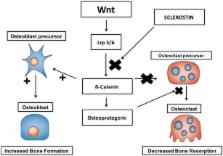
Diabetes complications and osteoporotic fractures are two of the most important causes of morbidity and mortality in older patients and share many features including genetic susceptibility, molecular mechanisms, and environmental factors. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) compromises bone microarchitecture by inducing abnormal bone cell function and matrix structure, with increased osteoblast apoptosis, diminished osteoblast differentiation, and enhanced osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. The linkage between these two chronic diseases creates a possibility that certain antidiabetic therapies may affect bone quality. Both glycemic and bone homeostasis are under control of common regulatory factors. These factors include insulin, accumulation of advanced glycation end products, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, gastrointestinal hormones (such as the glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide and the glucagon-like peptides 1 and 2), and bone-derived hormone osteocalcin. This background allows individual pharmacological targets for antidiabetic therapies to affect the bone quality due to their indirect effects on bone cell differentiation and bone remodeling process. Moreover, it’s important to consider the fragility fractures as another diabetes complication and discuss more deeply about the requirement for adequate screening and preventive measures. This review aims to briefly explore the impact of T2DM on bone metabolic and mechanical proprieties and fracture risk.
Related collections
Most cited references49
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
In vivo assessment of bone quality in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Bone mineral density and fracture risk in type-2 diabetes mellitus: the Rotterdam Study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found