- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparative Evaluation of Four Different Obturating Techniques in Primary Teeth Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography: An In Vivo Study
Read this article at
A bstract
Background
The quality of the obturation plays a significant role in the success of endodontic treatment. To date, various technologies have been used to evaluate the quality of obturation, but all of them have their own limitations. In order to overcome those limitations, recent technological advancements like cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) can be helpful.
Aim
To compare and evaluate the efficiency of different root canal obturation techniques in primary teeth using CBCT.
Materials and methods
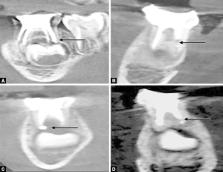
A total of 80 root canals in 30 children aged between 4 and 9 years were selected and divided into four groups, with 20 root canals in each. Obturation in group I was performed using the endodontic pressure syringe; group II—hand spreaders; group III—Lentulo spirals mounted on slow-speed handpiece; and group IV—insulin syringe. The quality of obturation was evaluated using a CBCT scan.
Results
Group I samples showed the most optimally filled canals followed by II and III; least in group IV. A maximum number of overfilled canals was exhibited in group III samples. Voids were minimal in all four groups and the values obtained were not statistically significant.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Predicting pulpectomy success and its relationship to exfoliation and succedaneous dentition.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cone Beam Computed Tomography - Know its Secrets
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found