- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Correlation Among Serum Calcidiol, Sun Index, and Vitamin D Intake in Individuals With Seborrheic Keratoses Living in Coastal Area
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Seborrheic keratoses (SK) are benign epidermal tumors with high sun exposure as a major risk factor. Vitamin D deficiency is also thought to play a role in its pathogenesis. There has been no data regarding SK, calcidiol level, vitamin D intake, and sun index (SI) among people living in coastal areas in Indonesia.
Objectives
To assess the correlation between 1) serum calcidiol levels with SI and vitamin D intake and 2) lesion size with SI and serum calcidiol level among SK patients living in a coastal area.
Methods
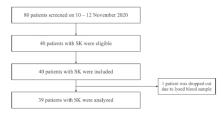
This is a cross-sectional study. We performed interviews using the sun index questionnaire and semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire for vitamin D; physical examination; dermoscopy to determine the largest SK lesion size; and measurement of serum calcidiol levels in participants with SK living in Cilincing District, North Jakarta. Spearman correlation test was used to assess the relationship between variables.
Results
Thirty-nine participants with SK aged 19–59 years were analyzed. The median of the SK largest diameter, SI, serum calcidiol, and vitamin D intake was 2 (1–10) mm, 3.95 (1.1–23.52), 14.3 (5.25–35.30) ng/ml, and 4.3 (0.1–30.1) mcg/day, respectively. SI and vitamin D intake were not significantly correlated with calcidiol levels. Similarly, SI and calcidiol levels were not significantly correlated with the largest SK lesion size.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found