- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Preparation of Microfiltration Hollow Fiber Membranes from Cellulose Triacetate by Thermally Induced Phase Separation
Read this article at
Abstract

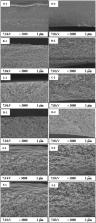
For the first time, self-standing microfiltration (MF) hollow fiber membranes were prepared from cellulose triacetate (CTA) via the thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) method. The resultant membranes were compared with counterparts prepared from cellulose diacetate (CDA) and cellulose acetate propionate (CAP). Extensive solvent screening by considering the Hansen solubility parameters of the polymer and solvent, the polymer’s solubility at high temperature, solidification of the polymer solution at low temperature, viscosity, and processability of the polymeric solution, is the most challenging issue for cellulose membrane preparation. Different phase separation mechanisms were identified for CTA, CDA, and CAP polymer solutions prepared using the screened solvents for membrane preparation. CTA solutions in binary organic solvents possessed the appropriate properties for membrane preparation via liquid–liquid phase separation, followed by a solid–liquid phase separation (polymer crystallization) mechanism. For the prepared CTA hollow fiber membranes, the maximum stress was 3–5 times higher than those of the CDA and CAP membranes. The temperature gap between the cloud point and crystallization onset in the polymer solution plays a crucial role in membrane formation. All of the CTA, CDA, and CAP membranes had a very porous bulk structure with a pore size of ∼100 nm or larger, as well as pores several hundred nanometers in size at the inner surface. Using an air gap distance of 0 mm, the appropriate organic solvents mixed in an optimized ratio, and a solvent for cellulose derivatives as the quench bath media, it was possible to obtain a CTA MF hollow fiber membrane with high pure water permeance and notably high rejection of 100 nm silica nanoparticles. It is expected that these membranes can play a great role in pharmaceutical separation.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Microporous membrane formation via thermally induced phase separation. I. Solid-liquid phase separation
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Cellulose in NaOH–water based solvents: a review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found