- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Robotic-assisted compared with conventional total hip arthroplasty: systematic review and meta-analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Robotic-assisted total hip arthroplasty (THA) allows for accurate preoperative planning and component positioning, potentially enhancing implant survival and long-term outcomes. The relative efficacy and safety of robotic-assisted and conventional THA, however, are unclear. This systematic review and meta-analysis compared the safety and efficacy of robotic-assisted and conventional THA.
Methods
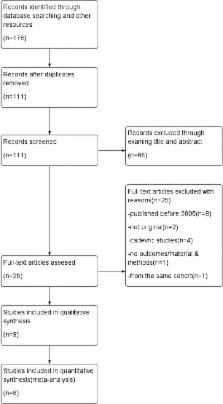
Medline, Embase and the Cochrane Library were comprehensively searched in September 2017 to identify studies comparing the safety and efficacy of robotic-assisted and conventional THA. Seven studies were included. Data of interest were extracted and analysed using Review Manager 5.3.
Results
The seven included studies involved 1516 patients, with 522 undergoing robotic-assisted and 994 undergoing conventional THA. Compared with conventional THA, robotic-assisted THA was associated with longer surgical time (not significant); lower intraoperative complication rates (OR: 0.12, 95% CI: 0.05 to 0.34, p<0.0001 I 2); better cup placement, stem placement and global offset and a higher rate of heterotopic ossifications. Functional scores, limb length discrepancy and rates of revision and stress shielding were similar in the two groups. The relative amount of blood loss was unclear.
Conclusion
The results of this meta-analysis suggest that robotic-assisted THA has certain advantages over conventional THA, including the results of component positioning and rates of intraoperative complications. Additional comparative studies are required to determine the long-term clinical outcomes of robotic-assisted THA.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The epidemiology of osteoarthritis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comparison of robotic-assisted and conventional acetabular cup placement in THA: a matched-pair controlled study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found