- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A global assessment of recent trends in gastrointestinal cancer and lifestyle‐associated risk factors

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancers were responsible for 26.3% of cancer cases and 35.4% of deaths worldwide in 2018. This study aimed to analyze the global incidence, mortality, prevalence, and contributing risk factors of the 6 major GI cancer entities [esophageal cancer (EC), gastric cancer (GC), liver cancer (LC), pancreatic cancer (PC), colon cancer, and rectal cancer].
Methods
Using the Global Cancer Observatory and the Global Health Observatory databases, we reviewed the current GI cancer incidence, prevalence, and mortality, analyzed the association of GI cancer prevalence with national human development indices (HDIs), identified the contributing risk factors, and estimated developing age‐ and sex‐specific trends in incidence and mortality.
Results
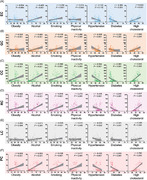
In 2020, the trend in age‐standardized rate of incidence of GI cancers closely mirrored that of mortality, with the highest rates of LC, EC, and GC in Asia and of colorectal cancer (CRC) and PC mainly in Europe. Incidence and mortality were positively, but the mortality‐to‐incidence ratio (MIR) was inversely correlated with the national HDI levels. High MIRs in developing countries likely reflected the lack of preventive strategies and effective treatments. GI cancer prevalence was highest in Europe and was also positively correlated with HDIs and lifestyle‐associated risk factors, such as alcohol consumption, smoking, obesity, insufficient physical activity, and high blood cholesterol level, but negatively correlated with hypertension and diabetes. Incidences of EC were consistently and those of GC mostly decreasing, whereas incidences of CRC were increasing in most countries/regions, especially in the younger populations. Incidences of LC and PC were also increasing in all age‐gender populations except for younger males. Mortalities were decreasing for EC, GC, and CRC in most countries/regions, and age‐specific trends were observed in PC and LC with a decrease in the younger but an increase in the older population.
Conclusions
On the global scale, higher GI cancer burden was accompanied, for the most part, by factors associated with the so‐called Western lifestyle reflected by high and very high national HDI levels. In countries/regions with very high HDI levels, patients survived longer, and increasing GI cancer cases were observed with increasing national HDI levels. Optimizing GI cancer prevention and improving therapies, especially for patients with comorbid metabolic diseases, are thus urgently recommended.
Abstract
Prevalence of gastrointestinal cancers was positively correlated with national human development index levels, but negatively with hypertension and diabetes rates. Age‐specific trends were observed in stomach cancer and esophagus cancer for incidence and in liver cancer and pancreatic cancer for mortality, as well as sex‐specific trends for stomach cancer and pancreatic cancer in the elder.These findings suggest that future research has to focus on the specific etiology of gastrointestinal cancers behind these epidemiologic transitions and improve therapeutic strategies for patients with comorbid metabolic diseases.
Related collections
Most cited references51
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found