- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Adjunctive air-polishing with erythritol in nonsurgical periodontal therapy: a randomized clinical trial

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
This study was aimed to investigate if the adjunctive use of erythritol air-polishing powder applied with the nozzle-system during subgingival instrumentation (SI) has an effect on the outcome of non-surgical periodontal treatment in patients with moderate to severe periodontitis.
Methods
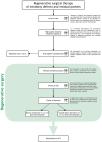
Fourty-two individuals with periodontitis received nonsurgical periodontal therapy by SI without (controls, n = 21) and with adjunctive air-polishing using nozzle + erythritol powder (test, n = 21). They were analyzed for the clinical variables BOP (primary outcome at six months), probing depth (PD), attachment level, four selected microorganisms and two biomarkers at baseline, before SI as well as three and six months after SI. Statistical analysis included nonparametric tests for intra- and intergroup comparisons.
Results
In both groups, the clinical variables PD, attachment level and BOP significantly improved three and six months after SI. The number of sites with PD ≥ 5 mm was significantly lower in the test group than in the control group after six months. At six months versus baseline, there were significant reductions of Tannerella forsythia and Treponema denticola counts as well as lower levels of MMP-8 in the test group.
Conclusions
Subgingival instrumentation with adjunctive erythritol air-polishing powder does not reduce BOP. But it may add beneficial effects like reducing the probing depth measured as number of residual periodontal pocket with PD ≥ 5 mm when compared with subgingival instrumentation only.
Clinical relevance
The adjunctive use of erythritol air-polishing powder applied with the nozzle-system during SI may improve the clinical outcome of SI and may reduce the need for periodontal surgery.
Trial registration The study was retrospectively registered in the German register of clinical trials, DRKS00015239 on 6th August 2018, https://www.drks.de/drks_web/navigate.do?navigationId=trial.HTML&TRIAL.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found