- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Tumor Microenvironment on a Chip: The Progress and Future Perspective
Read this article at
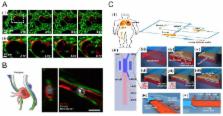
Abstract
Tumors develop in intricate microenvironments required for their sustained growth, invasion, and metastasis. The tumor microenvironment plays a critical role in the malignant or drug resistant nature of tumors, becoming a promising therapeutic target. Microengineered physiological systems capable of mimicking tumor environments are one emerging platform that allows for quantitative and reproducible characterization of tumor responses with pathophysiological relevance. This review highlights the recent advancements of engineered tumor microenvironment systems that enable the unprecedented mechanistic examination of cancer progression and metastasis. We discuss the progress and future perspective of these microengineered biomimetic approaches for anticancer drug prescreening applications.
Related collections
Most cited references76
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found