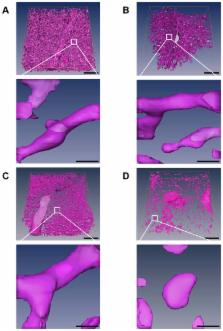
Background Much of our current understanding of microvascular permeability is based on the findings of classic experimental studies of blood capillary permeability to various-sized lipid-insoluble endogenous and non-endogenous macromolecules. According to the classic small pore theory of microvascular permeability, which was formulated on the basis of the findings of studies on the transcapillary flow rates of various-sized systemically or regionally perfused endogenous macromolecules, transcapillary exchange across the capillary wall takes place through a single population of small pores that are approximately 6 nm in diameter; whereas, according to the dual pore theory of microvascular permeability, which was formulated on the basis of the findings of studies on the accumulation of various-sized systemically or regionally perfused non-endogenous macromolecules in the locoregional tissue lymphatic drainages, transcapillary exchange across the capillary wall also takes place through a separate population of large pores, or capillary leaks, that are between 24 and 60 nm in diameter. The classification of blood capillary types on the basis of differences in the physiologic upper limits of pore size to transvascular flow highlights the differences in the transcapillary exchange routes for the transvascular transport of endogenous and non-endogenous macromolecules across the capillary walls of different blood capillary types. Methods The findings and published data of studies on capillary wall ultrastructure and capillary microvascular permeability to lipid-insoluble endogenous and non-endogenous molecules from the 1950s to date were reviewed. In this study, the blood capillary types in different tissues and organs were classified on the basis of the physiologic upper limits of pore size to the transvascular flow of lipid-insoluble molecules. Blood capillaries were classified as non-sinusoidal or sinusoidal on the basis of capillary wall basement membrane layer continuity or lack thereof. Non-sinusoidal blood capillaries were further sub-classified as non-fenestrated or fenestrated based on the absence or presence of endothelial cells with fenestrations. The sinusoidal blood capillaries of the liver, myeloid (red) bone marrow, and spleen were sub-classified as reticuloendothelial or non-reticuloendothelial based on the phago-endocytic capacity of the endothelial cells. Results The physiologic upper limit of pore size for transvascular flow across capillary walls of non-sinusoidal non-fenestrated blood capillaries is less than 1 nm for those with interendothelial cell clefts lined with zona occludens junctions (i.e. brain and spinal cord), and approximately 5 nm for those with clefts lined with macula occludens junctions (i.e. skeletal muscle). The physiologic upper limit of pore size for transvascular flow across the capillary walls of non-sinusoidal fenestrated blood capillaries with diaphragmed fenestrae ranges between 6 and 12 nm (i.e. exocrine and endocrine glands); whereas, the physiologic upper limit of pore size for transvascular flow across the capillary walls of non-sinusoidal fenestrated capillaries with open 'non-diaphragmed' fenestrae is approximately 15 nm (kidney glomerulus). In the case of the sinusoidal reticuloendothelial blood capillaries of myeloid bone marrow, the transvascular transport of non-endogenous macromolecules larger than 5 nm into the bone marrow interstitial space takes place via reticuloendothelial cell-mediated phago-endocytosis and transvascular release, which is the case for systemic bone marrow imaging agents as large as 60 nm in diameter. Conclusions The physiologic upper limit of pore size in the capillary walls of most non-sinusoidal blood capillaries to the transcapillary passage of lipid-insoluble endogenous and non-endogenous macromolecules ranges between 5 and 12 nm. Therefore, macromolecules larger than the physiologic upper limits of pore size in the non-sinusoidal blood capillary types generally do not accumulate within the respective tissue interstitial spaces and their lymphatic drainages. In the case of reticuloendothelial sinusoidal blood capillaries of myeloid bone marrow, however, non-endogenous macromolecules as large as 60 nm in diameter can distribute into the bone marrow interstitial space via the phago-endocytic route, and then subsequently accumulate in the locoregional lymphatic drainages of tissues following absorption into the lymphatic drainage of periosteal fibrous tissues, which is the lymphatic drainage of myeloid bone marrow. When the ultrastructural basis for transcapillary exchange across the capillary walls of different capillary types is viewed in this light, it becomes evident that the physiologic evidence for the existence of aqueous large pores ranging between 24 and 60 nm in diameter in the capillary walls of blood capillaries, is circumstantial, at best.