- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Physical activity of older children and adolescents in Germany – Results of the HBSC study 2022 and trends since 2009/10
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Physical activity is central to health, beginning in childhood and adolescence, and regular monitoring provides important information for strategic decisions on promoting physical activity in Germany.
Methods
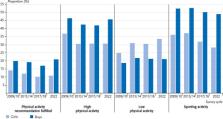
The current survey cycle of the Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study gives an insight into the prevalence of the indicators daily recommended physical activity, high and low physical activity, and sporting activity among students aged between 11 and 15 for 2022. In addition, the data is compared to the survey cycles of the 2009/10, 2013/14, and 2017/18 school years and analysed over time.
Results
The results of the current survey cycle show that 10.8 % of girls, 20.9 % of boys, and 12.4 % of gender diverse adolescents fulfil the daily physical activity recommendation. There are also major gender-specific differences for the other indicators. The group of gender diverse adolescents needs to be analysed further. The changes over time between 2009/10 and 2022 are relatively small. While girls’ physical activity habits decreased slightly for the various indicators between 2009/10 and 2022, boys’ prevalence remained relatively stable over the same period.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Global trends in insufficient physical activity among adolescents: a pooled analysis of 298 population-based surveys with 1·6 million participants
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Systematic review of the relationships between objectively measured physical activity and health indicators in school-aged children and youth.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
