- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
TGF-β1: Gentlemanly orchestrator in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (Review)

Read this article at
Abstract
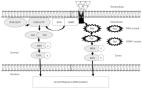
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a worldwide disease characterized by the chronic and irreversible decline of lung function. Currently, there is no drug to successfully treat the disease except for lung transplantation. Numerous studies have been devoted to the study of the fibrotic process of IPF and findings showed that transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) plays a central role in the development of IPF. TGF-β1 promotes the fibrotic process of IPF through various signaling pathways, including the Smad, MAPK, and ERK signaling pathways. There are intersections between these signaling pathways, which provide new targets for researchers to study new drugs. In addition, TGF-β1 can affect the fibrosis process of IPF by affecting oxidative stress, epigenetics and other aspects. Most of the processes involved in TGF-β1 promote IPF, but TGF-β1 can also inhibit it. This review discusses the role of TGF-β1 in IPF.
Related collections
Most cited references123
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found