- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Potential role of post-treatment follow-up FDG-PET CT to detect mandibular osteoradionecrosis: A case report
Read this article at
Abstract
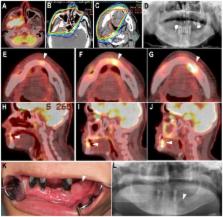
It was hypothesized that fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake on post-treatment follow-up positron emission tomography with computed tomography (PET CT; using PET CT to monitor and rule out recurrence and metastasis of head and neck carcinoma) would be useful for detecting and understanding the disease state of osteoradionecrosis (ORN) of the jaw. The present study included 14 patients who developed mandibular ORN following radiation therapy (RT) for head and neck cancer and underwent follow-up PET CT several times following RT. Areas exhibiting FDG uptake were retrospectively assessed on post-treatment follow-up PET CT images and were classified into three types: Spot type: Only spot accumulation of FDG; localized type: Accumulation of FDG restricted to within the bone resorption area; extensive type: Accumulation of FDG extending into surrounding soft tissue. PET classification at the time of clinical diagnosis of mandibular ORN in the 14 patients demonstrated the extensive type in 43%, localized type in 36% and spot type in 21%. An increased area of FDG uptake around the ORN was revealed retrospectively on post-treatment follow-up FDG PET-CT images in 50% of patients. Alterations in PET classification included spot type to localized type in 36% and localized type to extensive type in 14%. A significantly increased number of patients with extensive-type ORN (P=0.026) required surgery. Post-treatment follow-up FDG-PET CT may be useful for early detection and better understanding of ORN.
Related collections
Most cited references15
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Incidence and prevention of osteoradionecrosis after dental extraction in irradiated patients: a systematic review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for radionecrosis of the jaw: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial from the ORN96 study group.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found