- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Understanding different trajectories of mental health across the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The COVID-19 pandemic and nationally mandated restrictions to control the virus have been associated with increased mental health issues. However, the differential impact of the pandemic and lockdown on groups of individuals, and the personal characteristics associated with poorer outcomes are unknown.
Method
Data from 21 938 adults in England who participated in a stratified cohort study were analysed. Trajectories of depression and anxiety symptoms were identified using growth mixture modelling. Multinomial and logistic regression models were constructed to identify sociodemographic and personality-related risk factors associated with trajectory class membership.
Results
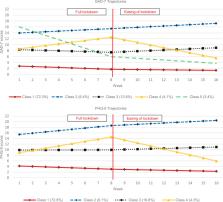
Four trajectories of depression and five for anxiety were identified. The most common group presented with low symptom severity throughout, other classes were identified that showed: severe levels of symptoms which increased; moderate symptoms throughout; worsening mental health during lockdown but improvements after lockdown ended; and for anxiety only, severe initial anxiety that decreased quickly during lockdown. Age, gender, ethnicity, income, previous diagnoses, living situation, personality factors and sociability were associated with different trajectories.
Conclusions
Nearly 30% of participants experienced trajectories with symptoms in the clinical range during lockdown, and did not follow the average curve or majority group, highlighting the importance of differential trajectories. Young, female, outgoing and sociable people and essential workers experienced severe anxiety around the announcement of lockdown which rapidly decreased. Younger individuals with lower incomes and previous mental health diagnoses experienced higher and increasing levels of symptoms. Recognising the likely symptom trajectories for such groups may allow for targeted care or interventions.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found