- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Host Molecules Regulating Neural Invasion of Zika Virus and Drug Repurposing Strategy
Read this article at
Abstract
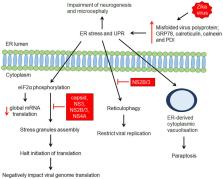
Zika virus (ZIKV) is a mosquito-borne, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus Flavivirus. Although ZIKV infection is usually known to exhibit mild clinical symptoms, intrauterine ZIKV infections have been associated with severe neurological manifestations, including microcephaly and Guillain Barre syndrome (GBS). Therefore, it is imperative to understand the mechanisms of ZIKV entry into the central nervous system (CNS) and its effect on brain cells. Several routes of neuro-invasion have been identified, among which blood–brain barrier (BBB) disruption is the commonest mode of access. The molecular receptors involved in viral entry remain unknown; with various proposed molecular ZIKV-host interactions including potential non-receptor mediated cellular entry. As ZIKV invade neuronal cells, they trigger neurotoxic mechanisms via cell-autonomous and non-cell autonomous pathways, resulting in neurogenesis dysfunction, viral replication, and cell death, all of which eventually lead to microcephaly. Together, our understanding of the biological mechanisms of ZIKV exposure would aid in the development of anti-ZIKV therapies targeting host cellular and/or viral components to combat ZIKV infection and its neurological manifestations. In this present work, we review the current understanding of ZIKV entry mechanisms into the CNS and its implications on the brain. We also highlight the status of the drug repurposing approach for the development of potential antiviral drugs against ZIKV.
Related collections
Most cited references115
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Guillain-Barré Syndrome outbreak associated with Zika virus infection in French Polynesia: a case-control study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found