- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clerodane diterpenoids with anti-inflammatory and synergistic antibacterial activities from Tinospora crispa
Read this article at
Abstract
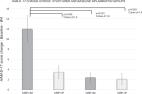
Compounds 5 and 7 exhibited nitric oxide release inhibitory activities with IC 50 values of 7.5 and 10.6 μM, respectively, and compounds 9 and 14 at the sub-MIC level significantly decreased the MIC of oxacillin against MRSA from 32.0 to 1.0 and 0.5 μg mL −1, respectively.
Abstract
Ten new and four known clerodane diterpenoids were isolated from the vine and leaves of Tinospora crispa. The chemical structures and absolute stereochemical configurations of all the compounds were established by spectroscopic methods and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis combined with electronic circular dichroism (ECD) analysis. All these compounds possess a lactone ring system except compound 10 which has a rare bridge ring between C-2 and C-20. The lactone ring in these compounds is diversely constructed between C-1 and C-18, C-6 and C-18, C-6 and C-17, C-12 and C-17, or C-15 and C-16 in the clerodane diterpenoid skeleton. All the compounds were assayed for their anti-inflammatory activities on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated microglial BV-2 cells. Compounds 5 and 7 exhibited nitric oxide (NO) release inhibitory activities with IC 50 values of 7.5 and 10.6 μM respectively. In particular, compound 7 exhibited better inhibitory activity and less cytotoxicity than the positive control minocycline. Moreover, compounds 9 and 14 were found to synergize with oxacillin (OXA) against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). This synergy was further confirmed by checkerboard and time-killing assays. Compounds 9 and 14 at the sub-MIC level significantly decreased the MIC of OXA from 32.0 to 1.0 μg mL −1 and 0.5 μg mL −1, respectively.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found