- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sex Determination in the Contemporary Chilean Population by Mandible Analysis in Panoramic Radiographies Translated title: Estimación Sexual de la Población Chilena Contemporánea Mediante Análisis de la Mandíbula en Radiografías Panorámicas
Read this article at
Abstract
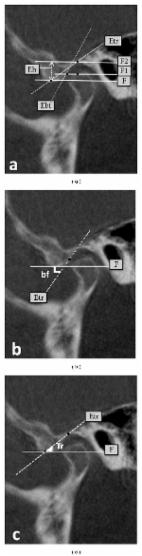
SUMMARY: Sex identification of a deceased human individual by means of the mandible is very important for forensic dentistry. The aim of the present study was to determine the sex of Chilean individuals by mandible analysis in panoramic radiographies. Linear and angular parameters of the mandible were analyzed from panoramic radiographies (PR). The study included PR of adult Chilean individuals, of both sexes, with optimum solution and contrast, and which allowed the angles and rami of the mandible to be viewed. Sex was determined by univariate and bivariate discriminant function analysis. The sample consisted of 594 PR of individuals aged between 18 and 84 years. The best sex predictor using univariate discriminant function analysis was the mandibular ramus height (MRH) (74.1 %), followed by the distance from the mental foramen - mandibular base (DMF-MB) (69.1 %) and the bicondylar breadth (BC) (66.7 %). The parameters that presented the lowest sex prediction were the angle of the mandible (AM) with 55.0 % and the distance between mental foramina (DMF) with 53.7 %. The best sex prediction was obtained by the step model of discriminant function analysis (80.2 %), including only three parameters: MRH, BC and DMF-MB. The parameters height of the mandibular ramus, bicondylar breadth and distance from the mental foramen - base of the mandible are good predictors of sex in Chilean individuals when used in conjunction; they are therefore indicated for sex determination in the contemporary Chilean population.
Translated abstract
RESUMEN: La identificación humana de un individuo fallecido a través de la mandíbula es muy relevante para la odontología forense. El objetivo de este estudio fue estimar el sexo de individuos Chilenos a través del análisis de la mandíbula, utilizando radiografías panorámicas. Fueron analizados parámetros lineales y angulares de la mandíbula, a través de radiografías panorámicas (RP). Se incluyeron RP de individuos chilenos adultos, ambos sexos, con solución y contraste óptimos, y que permitían la visualización de los ángulos y ramas de la mandíbula. Se realizó análisis por función discriminante univariada y bivariada para estimación del sexo. Fueron incluidas 594 RP de individuos entre 18 y 84 años. Para el análisis de función discriminante univariado, la altura de la rama mandibular (ARM) fue el parámetro más predictivo (74,1 %), seguido de la distancia foramen mentoniano - base de la mandíbula (DFM-BM) (69,1 %) y el ancho bicondilar (ABCo) (66,7 %). Los parámetros que presentaron menor predicción sexual fueron el ángulo de la mandíbula (AM) con un 55,0 % y la distancia inter-forámenes mentonianos (DIFM), con el 53.7 %. El análisis por pasos fue el modelo de análisis de función discriminante que presentó la mayor predicción sexual (79,5 %), en el cual fueron incluidos sólo tres parámetros: ARM, ABCo y DFM-BM. Los parámetros altura de la rama de la mandíbula, ancho bicondilar y distancia desde el foramen mentoniano hasta la base de la mandíbula son buenos predictores del sexo en individuos Chilenos cuando utilizados en conjunto y están indicados para estimar el sexo en la población chilena contemporánea.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Body size and body shape in early hominins - implications of the Gona pelvis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found