- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Asymptomatic Spontaneous Pneumopericardium, Pneumomediastinum, and Subcutaneous Emphysema: A Case Report of an Incidental Rare Presentation
Read this article at
Abstract
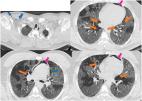
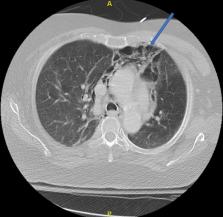
Pneumopericardium (PP), pneumomediastinum (PM), epidural pneumatosis, and subcutaneous emphysema (SE) are identified by the existence of free air or gas in the associated spaces. They are normally self-limited unless tension pneumothorax, tension PM, cardiac herniation, air tamponade, and esophageal rupture accompany these disorders. PM and PP can be divided into “spontaneous” or “secondary” based on the preceding etiologies. Spontaneous PM is often extremely rare and benign in course. On the other hand, secondary PM and PP are more common and result from intrathoracic infections, trauma-related esophageal rupture, or tears along the tracheobronchial tree. Our patient presented four days after a fall from a chair and was found to have suffered a stroke, with complete left side paralysis. CT imaging on arrival was significant for PM, PP, and SE, the cause of which remains unclear. The patient was diagnosed with COVID-pneumonia approximately six months prior to presentation. As the COVID-19 pandemic has evolved, several scientific papers have been published reporting infected patients who had developed spontaneous PT, PM, or even PP, in the absence of invasive mechanical ventilation. Is it possible that the spontaneous findings in our patient were COVID-related? Or could the spontaneous PP, PM, and SE be a sequel to the trauma of her fall from a chair? The answer still remains unclear.
Related collections
Most cited references11
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a comparative study and review of the literature.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found