- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of BAFF blockade on the B cell receptor repertoire and transcriptome in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease. Anti-B-cell-activating factor (BAFF) therapy effectively depletes B cells and reduces SLE disease activity. This research aimed to evaluate the effect of BAFF blockade on B cell receptor (BCR) repertoire and gene expression.
Methods
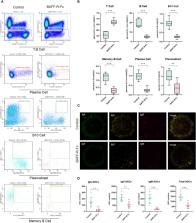
Through next-generation sequencing, we analyzed gene expression and BCR repertoire in MRL/lpr mice that received long-term anti-BAFF therapy. Based on gene expression profiles, we predicted the relative proportion of immune cells using ImmuCellAI-mouse, validating our predictions via flow cytometry and FluoroSpot.
Results
The loss of BCR repertoire diversity and richness, along with increased clonality and differential frequency distribution of the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) segment gene usage, were observed in BAFF-blockade mice. Meanwhile, the distribution of complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) length and CDR3 amino acid usage remained unaffected. BAFF blockade resulted in extensive changes in gene expression, particularly that of genes related to B cells and immunoglobulins. Besides, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α responses and interferon (IFN)-α/γ were downregulated, consistent with the decrease in IFN-γ and TNF-α serum levels following anti-BAFF therapy. In addition, BAFF blockade significantly reduced B cell subpopulations and plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and caused the depletion of antibody-secreting cells.
Related collections
Most cited references71
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Differential expression analysis for sequence count data

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found