- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Recent Trends in Hospitalization for Acute Myocardial Infarction in Beijing: Increasing Overall Burden and a Transition From ST-Segment Elevation to Non-ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction in a Population-Based Study
Read this article at
Abstract
Supplemental Digital Content is available in the text
Abstract
Comparable data on trends of hospitalization rates for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-STEMI (NSTEMI) remain unavailable in representative Asian populations.
To examine the temporal trends of hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and its subtypes in Beijing.
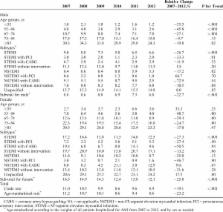
Patients hospitalized for AMI in Beijing from January 1, 2007 to December 31, 2012 were identified from the validated Hospital Discharge Information System. Trends in hospitalization rates, in-hospital mortality, length of stay (LOS), and hospitalization costs were analyzed by regression models for total AMI and for STEMI and NSTEMI separately. In total, 77,943 patients were admitted for AMI in Beijing during the 6 years, among whom 67.5% were males and 62.4% had STEMI. During the period, the rate of AMI hospitalization per 100,000 population increased by 31.2% (from 55.8 to 73.3 per 100,000 population) after age standardization, with a slight decrease in STEMI but a 3-fold increase in NSTEMI. The ratio of STEMI to NSTEMI decreased dramatically from 6.5:1.0 to 1.3:1.0. The age-standardized in-hospital mortality decreased from 11.2% to 8.6%, with a significant decreasing trend evident for STEMI in males and females ( P < 0.001) and for NSTEMI in males ( P = 0.02). The rate of percutaneous coronary intervention increased from 28.7% to 55.6% among STEMI patients. The total cost for AMI hospitalization increased by 56.8% after adjusting for inflation, although the LOS decreased by 1 day.
The hospitalization burden for AMI has been increasing in Beijing with a transition from STEMI to NSTEMI. Diverse temporal trends in AMI subtypes from the unselected “real-world” data in Beijing may help to guide the management of AMI in China and other developing countries.
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in China from 2001 to 2011 (the China PEACE-Retrospective Acute Myocardial Infarction Study): a retrospective analysis of hospital data.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Recent trends in the incidence, treatment, and outcomes of patients with STEMI and NSTEMI.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found