- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Second-order calibration applied to quantification of two active components of Schisandra chinensis in complex matrix
Read this article at
Abstract
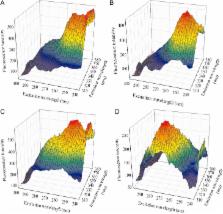
The effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) against various diseases urges more low cost, speed and sensitive analytical methods for investigating the phamacology of TCM and providing a theoretical basis for clinical use. The potential of second-order calibration method was validated for the quantification of two effective ingredients of Schisandra chinensis in human plasma using spectrofluorimetry. The results obtained in the present study demonstrate the advantages of this strategy for multi-target determination in complex matrices. Although the spectra of the analytes are similar and a large number of interferences also exist, second-order calibration method could predict the accurate concentrations together with reasonable resolution of spectral profiles for analytes of interest owing to its ‘second-order advantage’. Moreover, the method presented in this work allows one to simply experimental procedure as well as reduces the use of harmful chemical solvents.
Related collections
Most cited references28
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
PARAFAC. Tutorial and applications
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Asian medicine. The new face of traditional Chinese medicine.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found