- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Language Structures May Adapt to the Sociolinguistic Environment, but It Matters What and How You Count: A Typological Study of Verbal and Nominal Complexity
Read this article at
Abstract
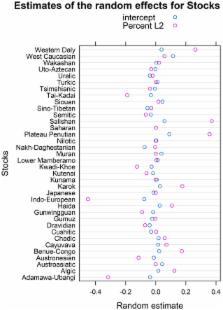
In this article we evaluate claims that language structure adapts to sociolinguistic environment. We present the results of two typological case studies examining the effects of the number of native (=L1) speakers and the proportion of adult second language (=L2) learners on language structure. Data from more than 300 languages suggest that testing the effect of population size and proportion of adult L2 learners on features of verbal and nominal complexity produces conflicting results on different grammatical features. The results show that verbal inflectional synthesis adapts to the sociolinguistic environment but the number of genders does not. The results also suggest that modeling population size together with proportion of L2 improves model fit compared to modeling them independently of one another. We thus argue that surveying population size alone may be insufficient to detect possible adaptation of linguistic structure to the sociolinguistic environment. Rather, other features, such as proportion of L2 speakers, prestige and social network density, should be studied, and if demographic numeric data are used, they should not be used in isolation but rather in competition with other sociolinguistic features. We also suggest that not all types of language structures within a given grammatical domain are equally sensitive to the effect of sociolinguistic variables, and that more exploratory studies are needed before we can arrive at a reliable set of grammatical features that may be potentially most (and least) adaptive to social structures.
Related collections
Most cited references51

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Conclusions beyond support: overconfident estimates in mixed models

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Language Structure Is Partly Determined by Social Structure
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found