- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Inhibitors
Abstract
Abstract:
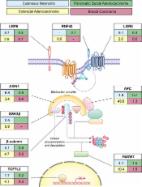
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the development, tissue ho-meostasis, angiogenesis, and carcinogenesis of cancer. Mutations and excessive activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer cells and cancer stem cells lead to drug resistance and recurrence of cancer in patients treated with conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Upregu-lation of proangiogenic factors is persistently induced by hyperactivated Wnt/β-catenin signaling during tumor angiogenesis. Furthermore, mutations and hyperactivated Wnt/β-catenin signaling are associated with worse outcomes in several human cancers, including breast cancer, cervical cancer, and glioma. Therefore, mutations and hyperactivation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling create challenges and limitations in cancer treatment. Recently, in silico drug design as well as high-throughput as-says and experiments have demonstrated the promising anticancer efficacy of chemotherapeutics, such as blocking the cancer cell cycle, inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and endothelial cell angi-ogenesis, inducing cancer cell apoptosis, removing cancer stem cells, and enhancing immune re-sponses. Compared to conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy, small-molecule inhibitors are considered the most promising therapeutic strategy for targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling path-way. Herein, we review the current small-molecule inhibitors of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling path-way, focusing on Wnt ligands, Wnt receptors, the β-catenin destruction complex, ubiquitin ligases and proteasomal destruction complex, β-catenin, β-catenin-associated transcriptional factors and co-activators, and proangiogenic factors. We describe the structure, mechanisms, and functions of these small molecules during cancer treatment in preclinical and clinical trials. We also review sev-eral Wnt/β-catenin inhibitors reported to exhibit anti-angiogenic effects. Finally, we explain various challenges in the targeting of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human cancer treatment and suggest potential therapeutic approaches to human cancer.
Related collections
Most cited references176
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Wnt signaling in cancer
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.