- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Occupational Risk Factors for Stroke: A Comprehensive Review
Read this article at
Abstract
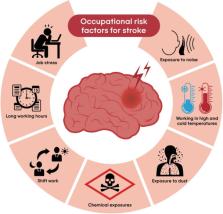
For primary prevention, it is important for public health and clinical medicine to identify and characterize modifiable risk factors of stroke. In existing literature, the impact of occupational variables on ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke has been extensively studied. This review summarizes the available data on the significance of occupational variables in stroke. The results of this review suggest that there is sufficient evidence for the relationship between increased risk of stroke and job stress, working in extreme temperatures, long working hours, and/or shift work. The association between long working hours and occupational exposure to noise and chemicals remains inconclusive although several studies have reported this finding. This review will act as a step toward future research and provide information that may serve as a baseline for developing targeted interventions to prevent stroke in the working population.
Related collections
Most cited references91
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global Burden of Stroke.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found