- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Evidence against Equimolarity of Large Repeat Arrangements and a Predominant Master Circle Structure of the Mitochondrial Genome from a Monkeyflower ( Mimulus guttatus) Lineage with Cryptic CMS
Read this article at
Abstract
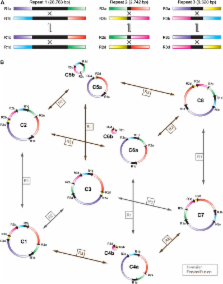
Despite intense investigation for over 25 years, the in vivo structure of plant mitochondrial genomes remains uncertain. Mapping studies and genome sequencing generally produce large circular chromosomes, whereas electrophoretic and microscopic studies typically reveal linear and multibranched molecules. To more fully assess the structure of plant mitochondrial genomes, the complete sequence of the monkeyflower ( Mimulus guttatus DC. line IM62) mitochondrial DNA was constructed from a large (35 kb) paired-end shotgun sequencing library to a high depth of coverage (∼30×). The complete genome maps as a 525,671 bp circular molecule and exhibits a fairly conventional set of features including 62 genes (encoding 35 proteins, 24 transfer RNAs, and 3 ribosomal RNAs), 22 introns, 3 large repeats (2.7, 9.6, and 29 kb), and 96 small repeats (40–293 bp). Most paired-end reads (71%) mapped to the consensus sequence at the expected distance and orientation across the entire genome, validating the accuracy of assembly. Another 10% of reads provided clear evidence of alternative genomic conformations due to apparent rearrangements across large repeats. Quantitative assessment of these repeat-spanning read pairs revealed that all large repeat arrangements are present at appreciable frequencies in vivo, although not always in equimolar amounts. The observed stoichiometric differences for some arrangements are inconsistent with a predominant master circular structure for the mitochondrial genome of M. guttatus IM62. Finally, because IM62 contains a cryptic cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) system, an in silico search for potential CMS genes was undertaken. The three chimeric open reading frames (ORFs) identified in this study, in addition to the previously identified ORFs upstream of the nad6 gene, are the most likely CMS candidate genes in this line.
Related collections
Most cited references73
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Insights into the evolution of mitochondrial genome size from complete sequences of Citrullus lanatus and Cucurbita pepo (Cucurbitaceae).
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found