- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
P(VDF-TrFE) nanofibers: structure of the ferroelectric and paraelectric phases through IR and Raman spectroscopies†
Read this article at
Abstract
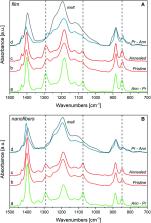
This study elucidates the complex morphology and the related spectroscopic response of poly(vinylidene fluoride- co-trifluoroethylene) copolymer, with 80% molar VDF content, namely P(VDF-TrFE) (80/20). We investigate the molecular structure, the morphology and the thermal behaviour of P(VDF-TrFE) samples obtained as electrospun nanofibers; we discuss their thermal evolution crossing the Curie temperature and the structure resulting after annealing, giving a comparison with P(VDF-TrFE) films. The new experimental data here obtained, combined with previous spectroscopic studies carried out on piezoelectric fluorinated polymers and copolymers, allow identifying spectroscopic markers sensitive to the molecular structure, the molecular orientation, the conformational defects and the kind of crystalline phase. We assign the vibrational modes localized on TrFE units by combining experimental observation and density functional calculations carried out on suitable molecular models. This work provides a sound set of diagnostic tools, which can be exploited for the assessment of structure/property relationships aimed at clarifying the molecular mechanisms leading to the piezoelectric performance of fluorinated copolymers.
Abstract
This study elucidates the complex morphology and the related spectroscopic response of poly(vinylidene fluoride- co-trifluoroethylene) copolymer, with 80% molar VDF content, namely P(VDF-TrFE) (80/20).

Related collections
Most cited references83
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The Piezoelectricity of Poly (vinylidene Fluoride)
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found