- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Emerging Role of Hydrogels in Drug Delivery Systems, Tissue Engineering and Wound Management
Read this article at
Abstract
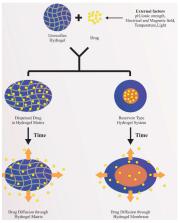
The popularity of hydrogels as biomaterials lies in their tunable physical properties, ability to encapsulate small molecules and macromolecular drugs, water holding capacity, flexibility, and controllable degradability. Functionalization strategies to overcome the deficiencies of conventional hydrogels and expand the role of advanced hydrogels such as DNA hydrogels are extensively discussed in this review. Different types of cross-linking techniques, materials utilized, procedures, advantages, and disadvantages covering hydrogels are tabulated. The application of hydrogels, particularly in buccal, oral, vaginal, and transdermal drug delivery systems, are described. The review also focuses on composite hydrogels with enhanced properties that are being developed to meet the diverse demand of wound dressing materials. The unique advantages of hydrogel nanoparticles in targeted and intracellular delivery of various therapeutic agents are explained. Furthermore, different types of hydrogel-based materials utilized for tissue engineering applications and fabrication of contact lens are discussed. The article also provides an overview of selected examples of commercial products launched particularly in the area of oral and ocular drug delivery systems and wound dressing materials. Hydrogels can be prepared with a wide variety of properties, achieving biostable, bioresorbable, and biodegradable polymer matrices, whose mechanical properties and degree of swelling are tailored with a specific application. These unique features give them a promising future in the fields of drug delivery systems and applied biomedicine.
Related collections
Most cited references202
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found