- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Regulation of Placental Extravillous Trophoblasts by the Maternal Uterine Environment
Read this article at
Abstract
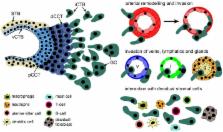
During placentation invasive extravillous trophoblasts (EVTs) migrate into the maternal uterus and modify its vessels. In particular, remodeling of the spiral arteries by EVTs is critical for adapting blood flow and nutrient transport to the developing fetus. Failures in this process have been noticed in different pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, intrauterine growth restriction, stillbirth, or recurrent abortion. Upon invasion into the decidua, the endometrium of pregnancy, EVTs encounter different maternal cell types such as decidual macrophages, uterine NK (uNK) cells and stromal cells expressing a plethora of growth factors and cytokines. Here, we will summarize development of the EVT lineage, a process occurring independently of the uterine environment, and formation of its different subtypes. Further, we will discuss interactions of EVTs with arteries, veins and lymphatics and illustrate how the decidua and its different immune cells regulate EVT differentiation, invasion and survival. The present literature suggests that the decidual environment and its soluble factors critically modulate EVT function and reproductive success.
Related collections
Most cited references237
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Tissue-Resident Macrophage Ontogeny and Homeostasis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found