- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
ROS-induced Oxidative Injury involved in Pathogenesis of Fungal Keratitis via p38 MAPK Activation
Read this article at
Abstract
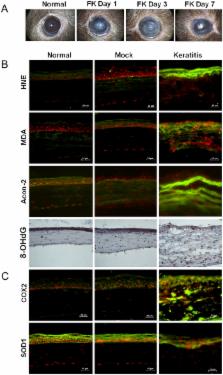
This study was to explore the mechanism by which reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced oxidative stress involved in the pathogenesis of fungal keratitis using an in vivo experimental keratitis mouse model and an in vitro culture model of human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs). Compared to normal control mice and HCECs, ROS production was markedly increased in fungal corneas and HCECs exposed to Candida albicans, accompanied by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) activation. Increased products of oxidative markers, malondialdehyde (MDA), 4–hydroxynonenal (HNE), mitochondria DNA 8-OHdG and aconitase-2 were observed in fungal infected corneas and HCECs. Fungal infection also increased the mRNA expression and protein production of heme oxygenase-1 (HMOX1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), with suppressed levels of antioxidant enzymes, superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD1), glutathione peroxidase-1 (GPx1) and peroxiredoxin-4 (PRDX4). Interestingly, the levels of ROS, oxidative markers and oxygenases were significantly reduced by co-cultured p38 inhibitor SB203580. Furthermore, SB203580 restored the levels of antioxidant enzymes suppressed by fungus. Our findings demonstrated for the first time that ROS-induced oxidative injury is involved in pathogenesis of fungal keratitis via p38 MAPK pathway, suggesting the novel therapeutic targets for the potential treatment of fungal keratitis.
Related collections
Most cited references52

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Oxidative Stress, Prooxidants, and Antioxidants: The Interplay
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal: a product and mediator of oxidative stress.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found