- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Beneficial effects of L-arginine on 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neuronal degeneration in substantia nigra of Balb/c mice
Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
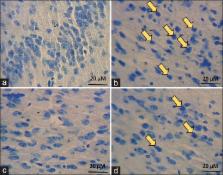
L-arginine has been recently investigated and proposed to reduce neurological damage after various experimental models of neuronal cellular damage. In this study, we aim to evaluate the beneficial effects of L-arginine administration on the numerical density of dark neurons (DNs) in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) of Balb/c mice subjected to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) administration.
Materials and Methods:
Male Balb/c mice were randomly divided into 4 groups ( n = 7 each): MPTP only; saline only (control); MPTP + L-arginine; and L-arginine only. The animals were infused intranasally with a single intranasal administration of the proneurotoxin MPTP (1 mg/nostril). L-arginine (300 mg/kg) was administrated intraperitoneally once daily for 1-week starting from 3 days after MPTP administration. Cavalieri principle method was used to estimate the numerical density of DNs in the SNc of different studied groups.
Results:
Twenty days following MPTP administration, the number of DNs was significantly increased when compared to sham-control and L-arginine-control groups ( P < 0.05). Nevertheless, our results showed that L-arginine administration significantly decreased the numerical density of DNs in SNc of mice.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Nitric oxide signaling in the central nervous system.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found