- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Bamboo leaf flavone changed the community of cecum microbiota and improved the immune function in broilers
Read this article at
Abstract
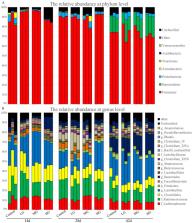
It has been shown that bamboo leaf flavone (BLF) displays biological and pharmacological activities in mammals. However, the effects of BLF on broiler gut microbiota and related immune function have not been investigated. The aim of this study was to test our hypothesis that BLF can improve the health status of broilers by modulating the gut microbiota. A total of 300 one-day-old Arbor Acres (AA) broilers were used to characterize their gut microbiota and immune status after feeding diet supplemented with BLF. The V4 hypervariable region of the 16S rRNA gene from cecal bacteria was sequenced via the Illumina MiSeq platform. The Immune status and related parameters were assessed, including the immune organ index (the spleen, thymus, and bursa), serum concentrations of IL-2 and INF-γ, and spleen IL-2 and INF-γ gene expressions. The results showed the BLF diet had an Immune enhancement effect on broilers. In addition, BFL caused the changes of the gut microbial community structure, resulting in greater proportions of bacterial taxa belonging to Lactobacillus, Clostridiales, Ruminococcus, and Lachnospiraceae. These bacteria have been used as probiotics for producing short chain fatty acids in hosts. These results indicate that BLF supplement improves immune function in chicken via modulation of the gut microbiota.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The microbial metabolite desaminotyrosine protects from influenza through type I interferon
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Microbiota of the chicken gastrointestinal tract: influence on health, productivity and disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found