- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Serine Deficiency Exacerbates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in D-Galactose-Induced Aging Mice
Read this article at
Abstract
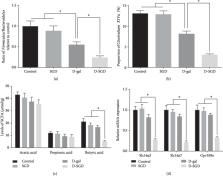
Inflammation and oxidative stress play key roles in the process of aging and age-related diseases. Since serine availability plays important roles in the support of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory defense system, we explored whether serine deficiency affects inflammatory and oxidative status in D-galactose-induced aging mice. Male mice were randomly assigned into four groups: mice fed a basal diet, mice fed a serine- and glycine-deficient (SGD) diet, mice injected with D-galactose and fed a basal diet, and mice injected with D-galactose and fed an SGD diet. The results showed that D-galactose resulted in oxidative and inflammatory responses, while serine deficiency alone showed no such effects. However, serine deficiency significantly exacerbated oxidative stress and inflammation in D-galactose-treated mice. The composition of fecal microbiota was affected by D-galactose injection, which was characterized by decreased microbiota diversity and downregulated ratio of Firmicutes/ Bacteroidetes, as well as decreased proportion of Clostridium XIVa. Furthermore, serine deficiency exacerbated these changes. Additionally, serine deficiency in combination with D-galactose injection significantly decreased fecal butyric acid content and gene expression of short-chain fatty acid transporters ( Slc16a3 and Slc16a7) and receptor ( Gpr109a) in the brain. Finally, serine deficiency exacerbated the decrease of expression of phosphorylated AMPK and the increase of expression of phosphorylated NF κB p65, which were caused by D-galactose injection. In conclusion, our results suggested that serine deficiency exacerbated inflammation and oxidative stress in D-galactose-induced aging mice. The involved mechanisms might be partially attributed to the changes in the microbiota-gut-brain axis affected by serine deficiency.
Related collections
Most cited references24

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Age‐related changes in the gut microbiota influence systemic inflammation and stroke outcome
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
[Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker].
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found