- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mathematical model calibrated to in vitro data predicts mechanisms of antiviral action of the influenza defective interfering particle “OP7”

Read this article at
Summary
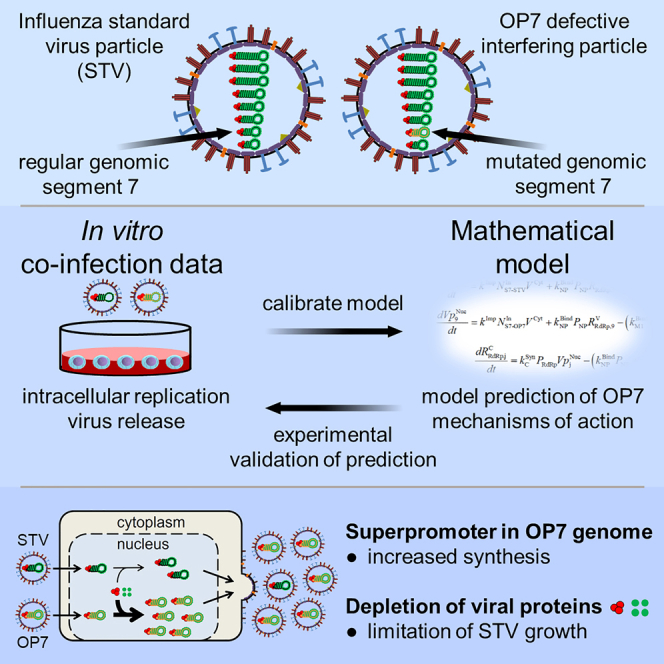
Defective interfering particles (DIPs) are regarded as potent broad-spectrum antivirals. We developed a mathematical model that describes intracellular co-infection dynamics of influenza standard virus (STV) and “OP7”, a new type of influenza DIP discovered recently. Based on experimental data from in vitro studies to calibrate the model and confirm its predictions, we deduce OP7’s mechanisms of interference, which were yet unknown. Simulations suggest that the “superpromoter” on OP7 genomic viral RNA enhances its replication and results in a depletion of viral proteins. This reduces STV genomic RNA replication, which appears to constitute an antiviral effect. Further, a defective viral protein (M1-OP7) likely causes the deficiency of OP7’s replication. It appears unable to bind to genomic viral RNAs to facilitate their nuclear export, a critical step in the viral life cycle. An improved understanding of OP7’s antiviral mechanism is crucial toward application in humans as a prospective antiviral treatment strategy.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
Abstract
Biological sciences; Biological sciences research methodologies; Natural sciences
Related collections
Most cited references90
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A new look at the statistical model identification
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found