- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Bcl-2 family proteins as regulators of cancer cell invasion and metastasis: a review focusing on mitochondrial respiration and reactive oxygen species
Read this article at
Abstract
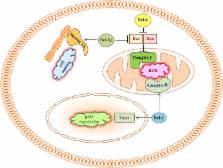
Although Bcl-2 family proteins were originally identified as key regulators of apoptosis, an impressive body of evidence has shown that pro-survival members of the Bcl-2 family, including Bcl-2, Bcl-X L, and Bcl-w, can also promote cell migration, invasion, and cancer metastasis. Interestingly, cell invasion was recently found to be suppressed by multidomain pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family, such as Bax and Bak. While the mechanisms underlying these new functions of Bcl-2 proteins are just beginning to be studied, reactive oxygen species (ROS) have emerged as inducers of cell invasion and the production of ROS from mitochondrial respiration is known to be promoted and suppressed by the pro-survival and multidomain pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members, respectively. Here, I review the evidence supporting the ability of Bcl-2 proteins to regulate cancer cell invasion and metastasis, and discuss our current understanding of their underlying mechanisms, with a particular focus on mitochondrial respiration and ROS, which could have implications for the development of strategies to overcome tumor progression.
Related collections
Most cited references77
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
FAK-Src signalling through paxillin, ERK and MLCK regulates adhesion disassembly.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found