- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Newly developed SYBR Green-based quantitative real-time PCRs revealed coinfection evidence of Angiostrongylus cantonensis and A. malaysiensis in Achatina fulica existing in Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand

Read this article at
Abstract
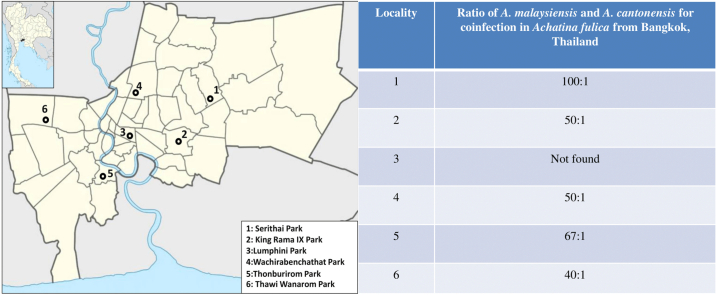
Angiostrongylus cantonensis is a well-known pathogen causing eosinophilic meningitis associated with angiostrongyliasis. Humans, as accidental hosts, are infected by consuming undercooked snails containing third-stage larvae. A. malaysiensis is closely related to A. cantonensis and has been described as a potential human pathogen. The two species distribution was recently reported to overlap in the same endemic area, particularly in the Indochina Peninsula. Similar morphological characteristics of the third-stage larva in the snail-intermediate host often lead to misidentification of the two species. Thus, we aimed to develop a sensitive and specific method to detect and discriminate Angiostrongylus third-stage larva by designing species-specific primers based on the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene. We developed the SYBR Green quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) method for two species-specific detection assays, which could be conducted simultaneously. The method was subsequently employed to detect and identify third-stage larvae of Angiostrongylus isolated from infected Achatina fulica collected from six public parks in Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand. The method was also a preliminary applied to detect parasite tissue debris in the patients' cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). SYBR Green qPCRs quantitatively detected approximately 10 −4 ng of genomic DNA from one larva, facilitating species-specific detection. Based on the pools of third-stage larvae isolated individually from the tissue of each infected A. fulica collected from the public parks, the qPCR results revealed that A. malaysiensis was the predominant species infecting 5.26% of the collected snails. In comparison, coinfection between A. malaysiensis and A. cantonensis was 5.97%, and no single infection of A. cantonensis was detected in A. fulica. Our SYBR Green qPCR method is a useful and inexpensive technique for A. cantonensis and A. malaysiensis discrimination, and the method has sufficient sensitivity to detect isolated larvae from a snail-intermediate host. The ratio of A. cantonensis and A. malaysiensis larvae infecting the snails can also be estimated simultaneously. Our qPCRs can be employed in a molecular survey of A. cantonensis and A. malaysiensis within intermediate hosts and for clinical diagnosis of angiostrongyliasis with CSF specimens in future studies.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
The SYBR Green qPCRs were developed to detect and discriminate Angiostrongylus third-stage larvae by designing species-specific primers based on the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene.
-
•
A. malaysiensis is the predominant species in Bangkok Metropolitan, Thailand.
-
•
Coinfection between A. cantonensis and A. malaysiensis has occurred in the Achatina fulica population in Bangkok
Related collections
Most cited references48

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
NCBI BLAST: a better web interface

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
OligoCalc: an online oligonucleotide properties calculator
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.