- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Eco-evolutionary significance of domesticated retroelements in microbial genomes
Read this article at
Abstract
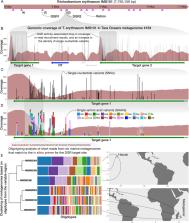
Since the first discovery of reverse transcriptase in bacteria, and later in archaea, bacterial and archaeal retroelements have been defined by their common enzyme that coordinates diverse functions. Yet, evolutionary refinement has produced distinct retroelements across the tree of microbial life that are perhaps best described in terms of their programmed RNA—a compact sequence that preserves core information for a sophisticated mechanism. From this perspective, reverse transcriptase has been selected as the modular tool for carrying out nature’s instructions in various RNA templates. Beneficial retroelements—those that can provide a fitness advantage to their host—evolved to their extant forms in a wide array of microorganisms and their viruses, spanning nearly all habitats. Within each specialized retroelement class, several universal features seem to be shared across diverse taxa, while specific functional and mechanistic insights are based on only a few model retroelement systems from clinical isolates. Currently, little is known about the diversity of cellular functions and ecological significance of retroelements across different biomes. With increasing availability of isolate, metagenome-assembled, and single-amplified genomes, the taxonomic and functional breadth of prokaryotic retroelements is coming into clearer view. This review explores the recently characterized classes of beneficial, yet accessory retroelements of bacteria and archaea. We describe how these specialized mechanisms exploit a form of fixed mobility, whereby the retroelements do not appear to proliferate selfishly throughout the genome. Moreover, we discuss computational approaches for systematic identification of retroelements from vast sequence repositories and highlight recent discoveries in terms of their apparent distribution and ecological significance in nature. Lastly, we present a new perspective on the eco-evolutionary significance of these genetic elements in marine bacteria and demonstrate approaches that enable the characterization of their environmental diversity through metagenomics.
Related collections
Most cited references37

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
scRNA-seq assessment of the human lung, spleen, and esophagus tissue stability after cold preservation
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Diverse enzymatic activities mediate antiviral immunity in prokaryotes
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found