- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Identification of a Multipotent Self-Renewing Stromal Progenitor Population during Mammalian Kidney Organogenesis

Read this article at
Summary
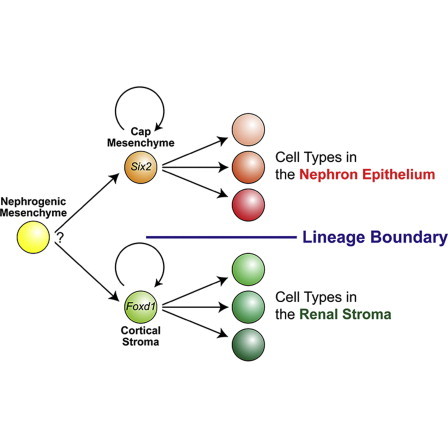
The mammalian kidney is a complex organ consisting of multiple cell types. We previously showed that the Six2-expressing cap mesenchyme is a multipotent self-renewing progenitor population for the main body of the nephron, the basic functional unit of the kidney. However, the cellular mechanisms establishing stromal tissues are less clear. We demonstrate that the Foxd1-expressing cortical stroma represents a distinct multipotent self-renewing progenitor population that gives rise to stromal tissues of the interstitium, mesangium, and pericytes throughout kidney organogenesis. Fate map analysis of Foxd1-expressing cells demonstrates that a small subset of these cells contributes to Six2-expressing cells at the early stage of kidney outgrowth. Thereafter, there appears to be a strict nephron and stromal lineage boundary derived from Six2-expressing and Foxd1-expressing cell types, respectively. Taken together, our observations suggest that distinct multipotent self-renewing progenitor populations coordinate cellular differentiation of the nephron epithelium and renal stroma during mammalian kidney organogenesis.
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
Abstract
Although progenitor populations for functional units of organs (also known as “parenchyma”) have been relatively well studied, origins of surrounding stromal cells are less clear in many organs, including the kidney. In this article, Kobayashi and colleagues discovered a multipotent self-renewing stromal progenitor population during mammalian kidney development.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Six2 defines and regulates a multipotent self-renewing nephron progenitor population throughout mammalian kidney development.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Temporally-controlled site-specific mutagenesis in the basal layer of the epidermis: comparison of the recombinase activity of the tamoxifen-inducible Cre-ER(T) and Cre-ER(T2) recombinases.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found