- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Global Trends and Hotspots in Research on Tooth Agenesis: A 20-Year Bibliometric Analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
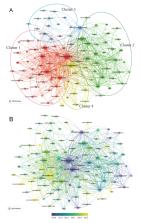
Tooth agenesis, one of the most common developmental defects in humans, not only impairs oral function but can also lead to craniofacial deformities. Bibliometric analysis can reveal significant shifts in research and publishing trends within specific fields. This study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the research hotspots in tooth agenesis and predict future trends through bibliometric analysis. We searched for English-language publications related to tooth agenesis from 2001 to 2021 on the Web of Science. The publications were limited to original and review articles, and bibliometric parameters such as publication year, country, institution, author, journal, citations, and keywords were extracted and analyzed using VOSviewer, Microsoft Excel 2010, and CiteSpace. A total of 2,287 papers were ultimately selected. The results show that the USA holds a leading position in the field of tooth agenesis research. A total of 9,803 authors participated in these studies, with Alexandre R Vieira from the USA being the most prolific and most cited author. This study indicates that multidisciplinary management has become the consensus first choice for treating dental agenesis. Gene mutations related to tooth agenesis continue to be a research hotspot attracting scholarly attention. Exploring the relationship between tooth agenesis and cancer may be a future research direction. These findings contribute to potential collaborations among experts in future research on the genetic causes of tooth agenesis and tumor development and to assist the scientific community by identifying research gaps in this field.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A meta-analysis of the prevalence of dental agenesis of permanent teeth.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mutations in AXIN2 cause familial tooth agenesis and predispose to colorectal cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found