- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
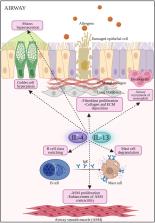
IL-4/IL-13 axis as therapeutic targets in allergic rhinitis and asthma
Read this article at
Abstract
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a common disorder of the upper airway, while asthma is a disease affecting the lower airway and both diseases are usually comorbid. Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 are critical cytokines in the induction of the pathogenic Th2 responses in AR and asthma. Targeting the IL-4/IL-13 axis at various levels of its signaling pathway has emerged as promising targeted therapy in both AR and asthma patient populations. In this review, we discuss the biological characteristics of IL-4 and IL-13, their signaling pathways, and therapeutic antibodies against each cytokine as well as their receptors. In particular, the pleiotropic roles of IL-4 and IL-13 in orchestrating Th2 responses in AR and asthma patients indicate that dual IL-4/IL-13 blockade is a promising therapeutic strategy for both diseases.
Related collections
Most cited references103
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
T-helper type 2-driven inflammation defines major subphenotypes of asthma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Moderate-to-Severe Uncontrolled Asthma
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found