- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Use of Changestat for Growth Rate Studies of Gut Microbiota
Read this article at
Abstract
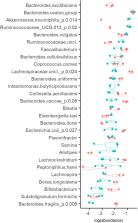
Human colon microbiota, composed of hundreds of different species, is closely associated with several health conditions. Controlled in vitro cultivation and up-to-date analytical methods make possible the systematic evaluation of the underlying mechanisms of complex interactions between the members of microbial consortia. Information on reproducing fecal microbial consortia can be used for various clinical and biotechnological applications. In this study, chemostat and changestat cultures were used to elucidate the effects of the physiologically relevant range of dilution rates on the growth and metabolism of adult fecal microbiota. The dilution rate was kept either at D = 0.05 or D = 0.2 1/h in chemostat cultures, while gradually changing from 0.05 to 0.2 1/h in the A-stat and from 0.2 to 0.05 1/h in the De-stat. Apple pectin as a substrate was used in the chemostat experiments and apple pectin or birch xylan in the changestat experiments, in the presence of porcine mucin in all cases. The analyses were comprised of HPLC for organic acids, UPLC for amino acids, GC for gas composition, 16S-rDNA sequencing for microbial composition, and growth parameter calculations. It was shown that the abundance of most bacterial taxa was determined by the dilution rate on both substrates. Bacteroides ovatus, Bacteroides vulgatus, and Faecalibacterium were prevalent within the whole range of dilution rates. Akkermansia muciniphila and Ruminococcaceae UCG-013 were significantly enriched at D = 0.05 1/h, while Bacteroides caccae, Lachnospiraceae unclassified and Escherichia coli clearly preferred D = 0.2 1/h. In the chemostat cultures, the production of organic acids and gases from pectin was related to the dilution rate. The ratio of acetate, propionate and butyrate was 5:2:1 ( D = 0.05 1/h) and 14:2:1 ( D = 0.2 1/h). It was shown that the growth rate-related characteristics of the fecal microbiota were concise in both directions between D = 0.05 and 0.2 1/h. Reproducible adaptation of the fecal microbiota was shown in the continuous culture with a changing dilution rate: changestat. Consortia cultivation is a promising approach for research purposes and several biotechnological applications, including the production of multi-strain probiotics and fecal transplantation mixtures.
Related collections
Most cited references28

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Stool substitute transplant therapy for the eradication of Clostridium difficile infection: ‘RePOOPulating’ the gut
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
