- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
High‐Throughput Metal 3D Printing Pen Enabled by a Continuous Molten Droplet Transfer

Read this article at
Abstract
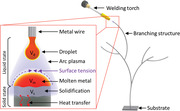
In metal additive manufacturing (AM), arc plasma is attracting attention as an alternative heat source to expensive lasers to enable the use of various metal wire materials with a high deposition efficiency. However, the stepwise material deposition and resulting limited number of degrees of freedom limit their potential for high‐throughput and large‐scale production for industrial applications. Herein, a high‐throughput metal 3D printing pen (M3DPen) strategy is proposed based on an arc plasma heat source by harnessing the surface tension of the molten metal for enabling continuous material deposition without a downward flow by gravity. The proposed approach differs from conventional arc‐based metal AM in that it controls the solidification and cooling time between interlayers of a point‐by‐point deposition path, thereby allowing for continuous metal 3D printing of freestanding and overhanging structures at once. The resulting mechanical properties and unique microstructures by continuous metal deposition that occur due to the difference in the thermal conditions of the molten metal under cooling are also investigated. This technology can be applied to a wide range of alloy systems and industrial manufacturing, thereby providing new possibilities for metal 3D printing.
Abstract
The arc plasma‐based M3DPen is capable of additively manufacturing line‐shaped metal structures by controlling the volume of molten droplets. Controlling the droplet volume and the solidification volume of the molten metal allows the surface tension to prevent the molten metal from flowing down due to gravity. Continuous and free metal AM is possible without requiring support and long cooling time.
Related collections
Most cited references2
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Book: not found