- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Reduction of facial pigmentation of melasma by topical lignin peroxidase: A novel fast-acting skin-lightening agent
Read this article at
Abstract
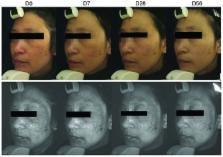
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lignin peroxidase (LIP) as a skin-lightening agent in patients with melasma. A self-controlled clinical study was performed in 31 women who had melasma on both sides of the face. This study involved 8 weeks of a full-face product treatment. The skin color was measured at days 0, 7, 28 and 56 using a chromameter on the forehead and cheeks. Standardized digital photographic images of each side of the face of all subjects were captured by a complexion analysis system. Clinical scores of the pigmentation were determined by two dermatologists. After using the LIP whitening lotion for 7 days, the luminance (L*) values of the melasma and the normal skin were significantly increased from baseline. The L* values continued to increase at days 28 and 56. The melasma area severity index (MASI) score was statistically decreased after 28 days of treatment. No treatment-related adverse events were observed. LIP whitening lotion was able to eliminate the skin pigmentation after 7 days of treatment, and provides a completely innovative approach to rapid skin lightening. The LIP whitening lotion exhibited good compatibility and was well tolerated.
Related collections
Most cited references16
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The melanogenesis and mechanisms of skin-lightening agents--existing and new approaches.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Melasma: a comprehensive update: part I.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found