- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Role of the Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p21 cip1/waf1 in Targeting Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutics
Read this article at
Abstract
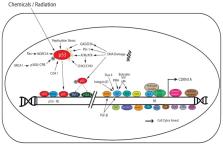
p21 cip1/waf1 mediates various biological activities by sensing and responding to multiple stimuli, via p53-dependent and independent pathways. p21 is known to act as a tumor suppressor mainly by inhibiting cell cycle progression and allowing DNA repair. Significant advances have been made in elucidating the potential role of p21 in promoting tumorigenesis. Here, we discuss the involvement of p21 in multiple signaling pathways, its dual role in cancer, and the importance of understanding its paradoxical functions for effectively designing therapeutic strategies that could selectively inhibit its oncogenic activities, override resistance to therapy and yet preserve its tumor suppressive functions.
Related collections
Most cited references133
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found