- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Auditory biological marker of concussion in children
Read this article at
Abstract
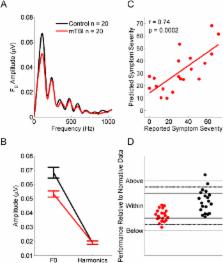
Concussions carry devastating potential for cognitive, neurologic, and socio-emotional disease, but no objective test reliably identifies a concussion and its severity. A variety of neurological insults compromise sound processing, particularly in complex listening environments that place high demands on brain processing. The frequency-following response captures the high computational demands of sound processing with extreme granularity and reliably reveals individual differences. We hypothesize that concussions disrupt these auditory processes, and that the frequency-following response indicates concussion occurrence and severity. Specifically, we hypothesize that concussions disrupt the processing of the fundamental frequency, a key acoustic cue for identifying and tracking sounds and talkers, and, consequently, understanding speech in noise. Here we show that children who sustained a concussion exhibit a signature neural profile. They have worse representation of the fundamental frequency, and smaller and more sluggish neural responses. Neurophysiological responses to the fundamental frequency partially recover to control levels as concussion symptoms abate, suggesting a gain in biological processing following partial recovery. Neural processing of sound correctly identifies 90% of concussion cases and clears 95% of control cases, suggesting this approach has practical potential as a scalable biological marker for sports-related concussion and other types of mild traumatic brain injuries.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in athletes: progressive tauopathy after repetitive head injury.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The epidemiology and impact of traumatic brain injury: a brief overview.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found