- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Music Therapy and Other Music-Based Interventions in Pediatric Health Care: An Overview
Read this article at
Abstract
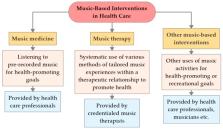
Background: In pediatric health care, non-pharmacological interventions such as music therapy have promising potential to complement traditional medical treatment options in order to facilitate recovery and well-being. Music therapy and other music-based interventions are increasingly applied in the clinical treatment of children and adolescents in many countries world-wide. The purpose of this overview is to examine the evidence regarding the effectiveness of music therapy and other music-based interventions as applied in pediatric health care. Methods: Surveying recent literature and summarizing findings from systematic reviews, this overview covers selected fields of application in pediatric health care (autism spectrum disorder; disability; epilepsy; mental health; neonatal care; neurorehabilitation; pain, anxiety and stress in medical procedures; pediatric oncology and palliative care) and discusses the effectiveness of music interventions in these areas. Results: Findings show that there is a growing body of evidence regarding the beneficial effects of music therapy, music medicine, and other music-based interventions for children and adolescents, although more rigorous research is still needed. The highest quality of evidence for the positive effects of music therapy is available in the fields of autism spectrum disorder and neonatal care. Conclusions: Music therapy can be considered a safe and generally well-accepted intervention in pediatric health care to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. As an individualized intervention that is typically provided in a person-centered way, music therapy is usually easy to implement into clinical practices. However, it is important to note that to exploit the potential of music therapy in an optimal way, specialized academic and clinical training and careful selection of intervention techniques to fit the needs of the client are essential.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Music interventions for improving psychological and physical outcomes in cancer patients.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Music interventions for preoperative anxiety.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found