- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Resolution of Neuroinflammation

Read this article at
Abstract
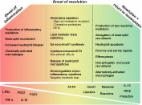
In the past few decades, as a result of their anti-inflammatory properties, n-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 LC-PUFAs), have gained greater importance in the regulation of inflammation, especially in the central nervous system (in this case known as neuroinflammation). If sustained, neuroinflammation is a common denominator of neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease and major depression, and of aging. Hence, limiting neuroinflammation is a real strategy for neuroinflammatory disease therapy and treatment. Recent data show that n-3 LC-PUFAs exert anti-inflammatory properties in part through the synthesis of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) such as resolvins, maresins and protectins. These SPMs are crucially involved in the resolution of inflammation. They could be good candidates to resolve brain inflammation and to contribute to neuroprotective functions and could lead to novel therapeutics for brain inflammatory diseases. This review presents an overview 1) of brain n-3 LC-PUFAs as precursors of SPMs with an emphasis on the effect of n-3 PUFAs on neuroinflammation, 2) of the formation and action of SPMs in the brain and their biological roles, and the possible regulation of their synthesis by environmental factors such as inflammation and nutrition and, in particular, PUFA consumption.
Related collections
Most cited references197
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Resolvins and protectins in inflammation resolution.